OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
SMA's Average
Return the average of simple moving averages with periods starting from min to max that is:
avg(sma(src,min),sma(src,min+1),...,sma(src,max))
The user can choose three types of weightings for the average, "simple", "linear", and "least squares".
Settings
Usage
The moving average can be used like any other classical moving average. The different types of weightings change the behavior of the moving average, the simple weighting will weight all the moving averages equally, a linear weighting will use the weighting function of a WMA, as such moving averages with lower periods will receive higher weights, this decrease the lag of the moving average. Finally, the least-squares weighting uses the weighting function of a least-squares moving average, this allows to drastically reduce the lag of the moving average.

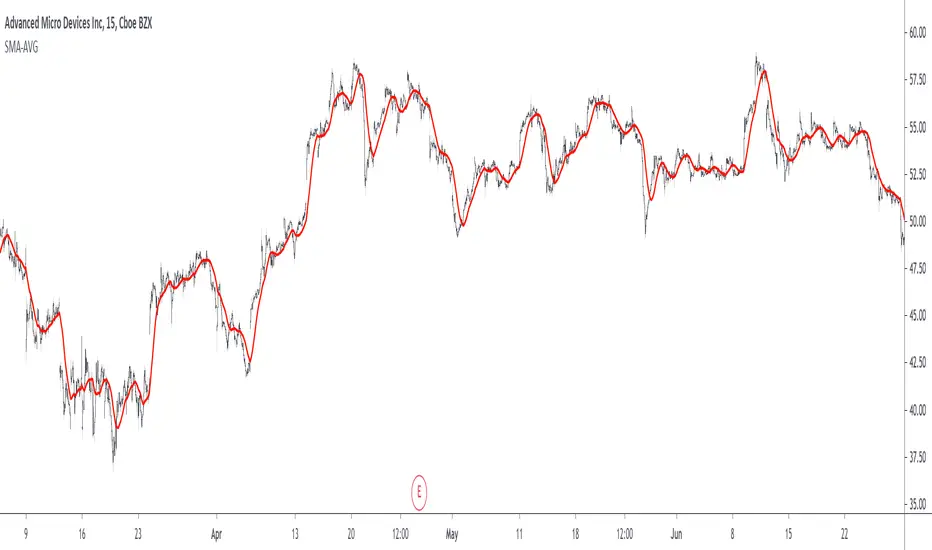
in red the moving average using simple weighting, in blue linear weighting, and in orange least squares weighting, with all using min = 14 and max = 28.

In red the moving average with min = 50 and max = 200, in blue a LSMA of period 200, notice how the moving average has less overshoots.
Details
Computing the average of various simple moving averages is simple, remember that a simple moving average can be computed using a cumulative sum:
Sma = change(cum(src),length)/length
we can't compute various "sma" functions with changing length argument within a for loop, but we can still differentiate within it, as such the cumulative sum method is super efficient and convenient.
The impulse response of this moving average is rectangular for the first "min" values, then the impulse is tailed, with the weighting method defining the shape of the tail.

in red the simple weighting method, in blue the linear method, and in orange the least-squares method.
Our moving average is an FIR moving average, as such the output lag is a linear characteristic of the moving average, which imply that:
Lag = Avg(lag(Sma(min)),lag(Sma(min+1))...,lag(max))
where lag is the lag of the moving average, in the case of a simple weighting we have:
Lag = Avg((min-1)/2,(min+1-1)/2,...,(max-1)/2) = Avg((min-1)/2,(max-1)/2)
a linear weighting gives a lag of:
Lag = Avg((min-1)/3,(min+1-1)/3,...,(max-1)/3) = Avg((min-1)/3,(max-1)/3)
Summary
A script computing the average of various moving averages has been presented, this MA might not be super useful to the everyday analyst but it stills have some great potential. Thx for reading.
This indicator is dedicated to my sister Lea, happy birthday kokoro
avg(sma(src,min),sma(src,min+1),...,sma(src,max))
The user can choose three types of weightings for the average, "simple", "linear", and "least squares".
Settings
- Min : minimum period of the sma
- Max : maximum period of the man, must be higher than "Min"
- Src : input data of the indicator
- Type : type of weighting, available options are "Simple", "Linear" or "Least Squares", by default "Simple"
Usage
The moving average can be used like any other classical moving average. The different types of weightings change the behavior of the moving average, the simple weighting will weight all the moving averages equally, a linear weighting will use the weighting function of a WMA, as such moving averages with lower periods will receive higher weights, this decrease the lag of the moving average. Finally, the least-squares weighting uses the weighting function of a least-squares moving average, this allows to drastically reduce the lag of the moving average.
in red the moving average using simple weighting, in blue linear weighting, and in orange least squares weighting, with all using min = 14 and max = 28.
In red the moving average with min = 50 and max = 200, in blue a LSMA of period 200, notice how the moving average has less overshoots.
Details
Computing the average of various simple moving averages is simple, remember that a simple moving average can be computed using a cumulative sum:
Sma = change(cum(src),length)/length
we can't compute various "sma" functions with changing length argument within a for loop, but we can still differentiate within it, as such the cumulative sum method is super efficient and convenient.
The impulse response of this moving average is rectangular for the first "min" values, then the impulse is tailed, with the weighting method defining the shape of the tail.
in red the simple weighting method, in blue the linear method, and in orange the least-squares method.
Our moving average is an FIR moving average, as such the output lag is a linear characteristic of the moving average, which imply that:
Lag = Avg(lag(Sma(min)),lag(Sma(min+1))...,lag(max))
where lag is the lag of the moving average, in the case of a simple weighting we have:
Lag = Avg((min-1)/2,(min+1-1)/2,...,(max-1)/2) = Avg((min-1)/2,(max-1)/2)
a linear weighting gives a lag of:
Lag = Avg((min-1)/3,(min+1-1)/3,...,(max-1)/3) = Avg((min-1)/3,(max-1)/3)
Summary
A script computing the average of various moving averages has been presented, this MA might not be super useful to the everyday analyst but it stills have some great potential. Thx for reading.
This indicator is dedicated to my sister Lea, happy birthday kokoro
开源脚本
秉承TradingView的精神,该脚本的作者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!您可以免费使用该脚本,但请记住,重新发布代码须遵守我们的网站规则。
Check out the indicators we are making at luxalgo: tradingview.com/u/LuxAlgo/
"My heart is so loud that I can't hear the fireworks"
"My heart is so loud that I can't hear the fireworks"
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并非旨在提供,也不构成TradingView提供或认可的任何形式的财务、投资、交易或其他类型的建议或推荐。请阅读使用条款了解更多信息。
开源脚本
秉承TradingView的精神,该脚本的作者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!您可以免费使用该脚本,但请记住,重新发布代码须遵守我们的网站规则。
Check out the indicators we are making at luxalgo: tradingview.com/u/LuxAlgo/
"My heart is so loud that I can't hear the fireworks"
"My heart is so loud that I can't hear the fireworks"
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并非旨在提供,也不构成TradingView提供或认可的任何形式的财务、投资、交易或其他类型的建议或推荐。请阅读使用条款了解更多信息。