OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Reynolds warning rate
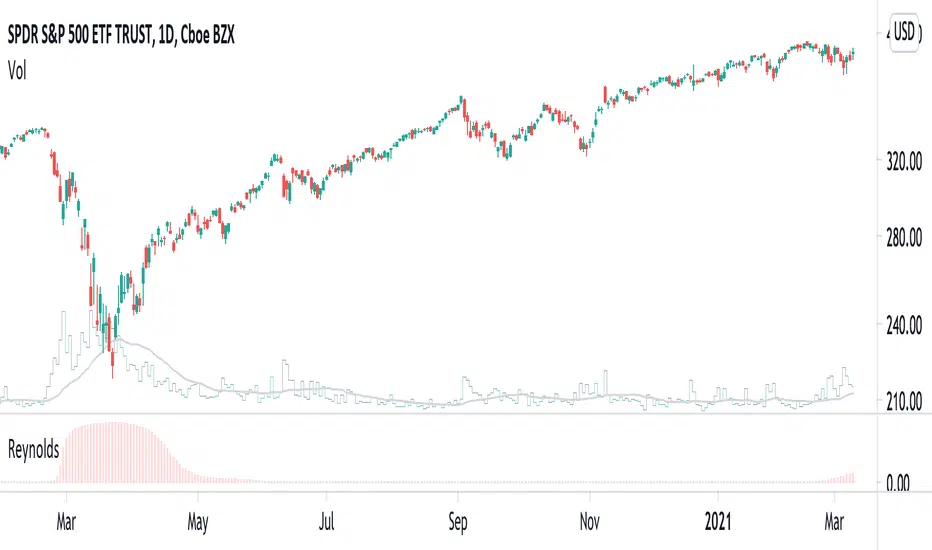
In fluid mechanics, the Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces within a fluid. Laminar flow occurs at low Reynolds numbers (i.e., viscous forces are dominant), whereas turbulent flow occurs at high Reynolds numbers (i.e., inertial forces are dominant). In the Turbulence indicator, I define that laminar flow occurs when simple moving averages have no interactions. In contrast, turbulent flow occurs when simple moving averages have chaotic interactions (i.e., irregular crossing and convergence).
Here, I calculate an economical analog of the Reynolds number developed by Jakimowicz and Juzwiszyn (2015). Furthermore, I propose the Reynolds Warning Rate, given by a ratio of short- and long-term Reynolds number.
The higher Reynolds Warning Rate indicates that price movement is going to a turbulence phase, and the market is under a possible systemic risk.
Reference:
Jakimowicz A, Juzwiszyn J (2015) Balance in the turbulent world of economy. Acta Physica Polonica A 127, 78–85.
Here, I calculate an economical analog of the Reynolds number developed by Jakimowicz and Juzwiszyn (2015). Furthermore, I propose the Reynolds Warning Rate, given by a ratio of short- and long-term Reynolds number.
The higher Reynolds Warning Rate indicates that price movement is going to a turbulence phase, and the market is under a possible systemic risk.
Reference:
Jakimowicz A, Juzwiszyn J (2015) Balance in the turbulent world of economy. Acta Physica Polonica A 127, 78–85.
开源脚本
本着TradingView的真正精神,此脚本的创建者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!虽然您可以免费使用它,但请记住,重新发布代码必须遵守我们的网站规则。
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并不意味着也不构成TradingView提供或认可的金融、投资、交易或其它类型的建议或背书。请在使用条款阅读更多信息。
开源脚本
本着TradingView的真正精神,此脚本的创建者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!虽然您可以免费使用它,但请记住,重新发布代码必须遵守我们的网站规则。
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并不意味着也不构成TradingView提供或认可的金融、投资、交易或其它类型的建议或背书。请在使用条款阅读更多信息。