OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA)
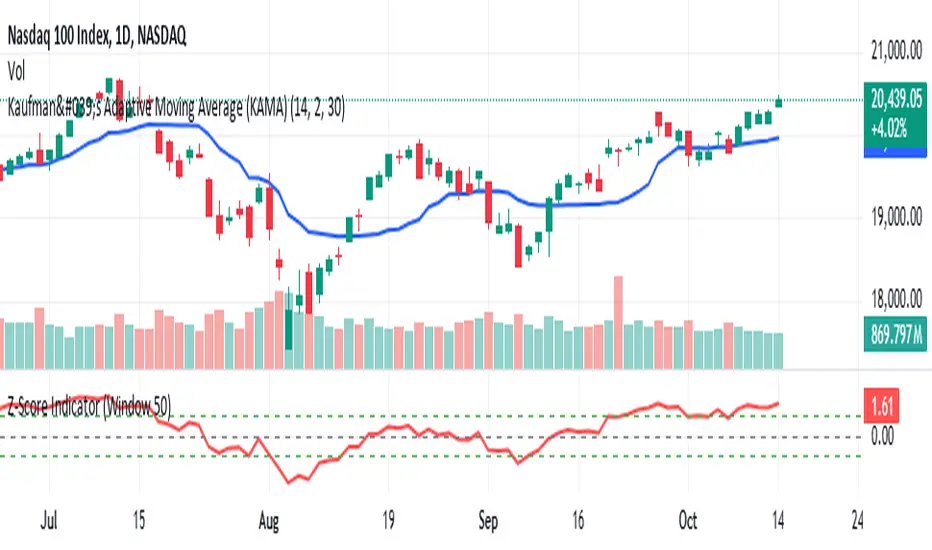
Another simple easy to use indicator that incorporates mean reversion and trend following.
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) is an indicator developed by Perry Kaufman that adjusts its sensitivity based on market volatility. It is designed to react more quickly during trending markets and slow down in sideways or volatile markets. The primary idea is that in a trending market, the moving average should be more sensitive to price changes, while in a non-trending market, it should be less responsive to noise.
KAMA Formula
The formula for the Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average is:
Efficiency Ratio (ER): Measures the efficiency of price movement over a given period.
ER
=
Smoothing Factor
Volatility
=
Sum of absolute price change
Sum of absolute price movement
ER=
Volatility
Smoothing Factor
=
Sum of absolute price movement
Sum of absolute price change
The Efficiency Ratio is calculated by taking the price change over a defined period and dividing it by the total price movement (which is the sum of absolute price changes).
Smoothing Constant (SC): This is a factor used to adjust the moving average's responsiveness:
SC
=
ER
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
+
(
1
−
ER
)
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
SC=ER×(2/(n+1))+(1−ER)×(2/(n+1))
where n is the length of the moving average period.
Steps to Calculate KAMA:
Efficiency Ratio (ER):
Calculate the sum of absolute price changes over the chosen period.
Calculate the sum of absolute price movements over the same period.
Smoothing Constant (SC):
Use the Efficiency Ratio to adjust the smoothing factor.
KAMA Calculation:
The initial KAMA is the simple moving average (SMA) of the first n periods.
For subsequent periods, KAMA is calculated using a formula based on the smoothing constant and previous KAMA values.
experiment with the variables as you like!!
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) is an indicator developed by Perry Kaufman that adjusts its sensitivity based on market volatility. It is designed to react more quickly during trending markets and slow down in sideways or volatile markets. The primary idea is that in a trending market, the moving average should be more sensitive to price changes, while in a non-trending market, it should be less responsive to noise.
KAMA Formula
The formula for the Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average is:
Efficiency Ratio (ER): Measures the efficiency of price movement over a given period.
ER
=
Smoothing Factor
Volatility
=
Sum of absolute price change
Sum of absolute price movement
ER=
Volatility
Smoothing Factor
=
Sum of absolute price movement
Sum of absolute price change
The Efficiency Ratio is calculated by taking the price change over a defined period and dividing it by the total price movement (which is the sum of absolute price changes).
Smoothing Constant (SC): This is a factor used to adjust the moving average's responsiveness:
SC
=
ER
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
+
(
1
−
ER
)
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
SC=ER×(2/(n+1))+(1−ER)×(2/(n+1))
where n is the length of the moving average period.
Steps to Calculate KAMA:
Efficiency Ratio (ER):
Calculate the sum of absolute price changes over the chosen period.
Calculate the sum of absolute price movements over the same period.
Smoothing Constant (SC):
Use the Efficiency Ratio to adjust the smoothing factor.
KAMA Calculation:
The initial KAMA is the simple moving average (SMA) of the first n periods.
For subsequent periods, KAMA is calculated using a formula based on the smoothing constant and previous KAMA values.
experiment with the variables as you like!!
开源脚本
秉承TradingView的精神,该脚本的作者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!您可以免费使用该脚本,但请记住,重新发布代码须遵守我们的网站规则。
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并非旨在提供,也不构成TradingView提供或认可的任何形式的财务、投资、交易或其他类型的建议或推荐。请阅读使用条款了解更多信息。
开源脚本
秉承TradingView的精神,该脚本的作者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!您可以免费使用该脚本,但请记住,重新发布代码须遵守我们的网站规则。
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并非旨在提供,也不构成TradingView提供或认可的任何形式的财务、投资、交易或其他类型的建议或推荐。请阅读使用条款了解更多信息。