OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Reverse Cutlers Relative Strength Index
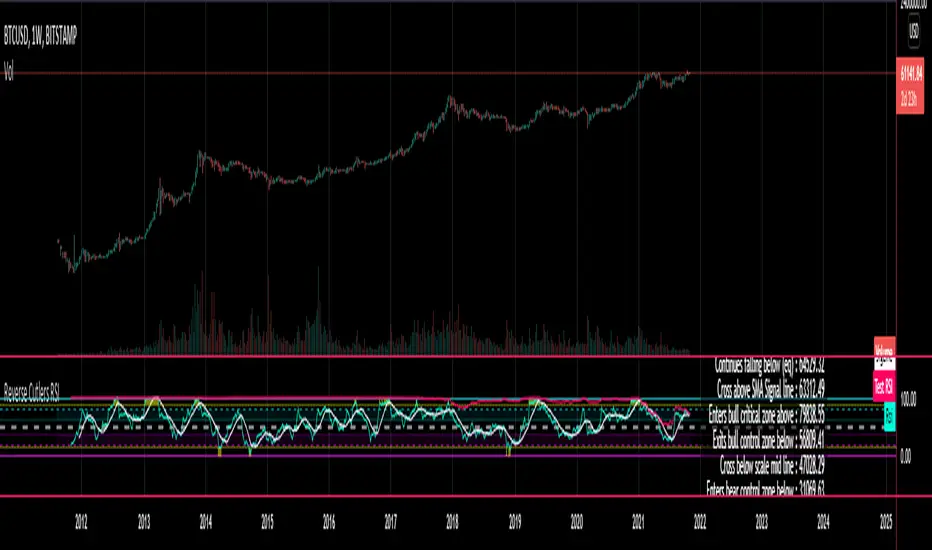
Introduction
The Reverse Cutlers Relative Strength Index (RCRSI) is an indicator which tells the user what price is required to give a particular Cutlers Relative Strength Index (RSI) value, or cross its Moving Average (MA) signal line.
Overview
Background & Credits:
The relative strength index (RSI) is a momentum indicator used in technical analysis that was originally developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr. and introduced in his seminal 1978 book, “New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems.”.
Cutler created a variation of the RSI known as “Cutlers RSI” using a different formulation to avoid an inherent accuracy problem which arises when using Wilders method of smoothing.
Further developments in the use, and more nuanced interpretations of the RSI have been developed by Cardwell, and also by well-known chartered market technician, Constance Brown C.M.T., in her acclaimed book "Technical Analysis for the Trading Professional” 1999 where she described the idea of bull and bear market ranges for RSI, and while she did not actually reveal the formulas, she introduced the concept of “reverse engineering” the RSI to give price level outputs.
Renowned financial software developer, co-author of academic books on finance, and scientific fellow to the Department of Finance and Insurance at the Technological Educational Institute of Crete, Giorgos Siligardos PHD. brought a new perspective to Wilder’s RSI when he published his excellent and well-received articles "Reverse Engineering RSI [A Wilder Variation]" and "Reverse Engineering RSI II [The Revenge of the Indicators]" in the June 2003, and August 2003 issues of Stocks & Commodities magazine, where he described his methods of reverse engineering Wilders RSI.
Several excellent Implementations of the Reverse Wilders Relative Strength Index have been published here on Tradingview and elsewhere.
My utmost respect, and all due credits to authors of related prior works.
Introduction
It is worth noting that while the general RSI formula, and the logic dictating the UpMove and DownMove data series as described above has remained the same as the Wilders original formulation, it has been interpreted in a different way by using a different method of averaging the upward, and downward moves.
Cutler recognized the issue of data length dependency when using wilders smoothing method of calculating RSI which means that wilders standard RSI will have a potential initialization error which reduces with every new data point calculated meaning early results should be regarded as unreliable until enough calculation iterations have occurred for convergence.
Hence Cutler proposed using Simple Moving Averaging for gain and loss data which this Indicator is based on.
Having "Reverse engineered" prices for any oscillator makes the planning, and execution of strategies around that oscillator far simpler, more timely and effective.
Introducing the Reverse Cutlers RSI which consists of plotted lines on a scale of 0 to 100, and an optional infobox.
The RSI scale is divided into zones:
• Scale high (100)
• Bull critical zone (80 - 100)
• Bull control zone (62 - 80)
• Scale midline (50)
• Bear critical zone (20 - 38)
• Bear control zone (0 - 20)
• Scale low (0)
The RSI plots are:
• Cutlers RSI
• RSI MA signal line
• Test price RSI
• Alert level high
• Alert level low
The info box displays output closing price levels where Cutlers RSI value will crossover:
• Its previous value. (RSI [1])
• Bull critical zone.
• Bull control zone.
• Mid-Line.
• Bear control zone.
• Bear critical zone.
• RSI MA signal line
• Alert level High
• Alert level low
And also displays the resultant RSI for a user defined closing price:
• Test price RSI
The infobox outputs can be shown for the current bar close, or the next bar close.
The user can easily select which information they want in the infobox from the setttings
Importantly:
All info box price levels for the current bar are calculated immediately upon the current bar closing and a new bar opening, they will not change until the current bar closes.
All info box price levels for the next bar are projections which are continually recalculated as the current price changes, and therefore fluctuate as the current price changes.
Understanding the Relative Strength Index
At its simplest the RSI is a measure of how quickly traders are bidding the price of an asset up or down.
It does this by calculating the difference in magnitude of price gains and losses over a specific lookback period to evaluate market conditions.
The RSI is displayed as an oscillator (a line graph that can move between two extremes) and outputs a value limited between 0 and 100.
It is typically accompanied by a moving average signal line.
Traditional interpretations
Overbought and oversold:
An RSI value of 70 or above indicates that an asset is becoming overbought (overvalued condition), and may be may be ready for a trend reversal or corrective pullback in price.
An RSI value of 30 or below indicates that an asset is becoming oversold (undervalued condition), and may be may be primed for a trend reversal or corrective pullback in price.
Midline Crossovers:
When the RSI crosses above its midline (RSI > 50%) a bullish bias signal is generated. (only take long trades)
When the RSI crosses below its midline (RSI < 50%) a bearish bias signal is generated. (only take short trades)
Bullish and bearish moving average signal Line crossovers:
When the RSI line crosses above its signal line, a bullish buy signal is generated
When the RSI line crosses below its signal line, a bearish sell signal is generated.
Swing Failures and classic rejection patterns:
If the RSI makes a lower high, and then follows with a downside move below the previous low, a Top Swing Failure has occurred.
If the RSI makes a higher low, and then follows with an upside move above the previous high, a Bottom Swing Failure has occurred.
Examples of classic swing rejection patterns
Bullish swing rejection pattern:
The RSI moves into oversold zone (below 30%).
The RSI rejects back out of the oversold zone (above 30%)
The RSI forms another dip without crossing back into oversold zone.
The RSI then continues the bounce to break up above the previous high.
Bearish swing rejection pattern:
The RSI moves into overbought zone (above 70%).
The RSI rejects back out of the overbought zone (below 70%)
The RSI forms another peak without crossing back into overbought zone.
The RSI then continues to break down below the previous low.
Divergences:
A regular bullish RSI divergence is when the price makes lower lows in a downtrend and the RSI indicator makes higher lows.
A regular bearish RSI divergence is when the price makes higher highs in an uptrend and the RSI indicator makes lower highs.
A hidden bullish RSI divergence is when the price makes higher lows in an uptrend and the RSI indicator makes lower lows.
A hidden bearish RSI divergence is when the price makes lower highs in a downtrend and the RSI indicator makes higher highs.
Regular divergences can signal a reversal of the trending direction.
Hidden divergences can signal a continuation in the direction of the trend.
Chart Patterns:
RSI regularly forms classic chart patterns that may not show on the underlying price chart, such as ascending and descending triangles & wedges, double tops, bottoms and trend lines etc.
Support and Resistance:
It is very often easier to define support or resistance levels on the RSI itself rather than the price chart.
Modern interpretations in trending markets:
Modern interpretations of the RSI stress the context of the greater trend when using RSI signals such as crossovers, overbought/oversold conditions, divergences and patterns.
Constance Brown, CMT, was one of the first who promoted the idea that an oversold reading on the RSI in an uptrend is likely much higher than 30%, and that an overbought reading on the RSI during a downtrend is much lower than the 70% level.
In an uptrend or bull market, the RSI tends to remain in the 40 to 90 range, with the 40-50 zone acting as support.
During a downtrend or bear market, the RSI tends to stay between the 10 to 60 range, with the 50-60 zone acting as resistance.
For ease of executing more modern and nuanced interpretations of RSI it is very useful to break the RSI scale into bull and bear control and critical zones.
These ranges will vary depending on the RSI settings and the strength of the specific market’s underlying trend.
Limitations of the RSI
Like most technical indicators, its signals are most reliable when they conform to the long-term trend.
True trend reversal signals are rare, and can be difficult to separate from false signals.
False signals or “fake-outs”, e.g. a bullish crossover, followed by a sudden decline in price, are common.
Since the indicator displays momentum, it can stay overbought or oversold for a long time when an asset has significant sustained momentum in either direction.
Data Length Dependency when using wilders smoothing method of calculating RSI means that wilders standard RSI will have a potential initialization error which reduces with every new data point calculated meaning early results should be regarded as unreliable until calculation iterations have occurred for convergence.
The Reverse Cutlers Relative Strength Index (RCRSI) is an indicator which tells the user what price is required to give a particular Cutlers Relative Strength Index (RSI) value, or cross its Moving Average (MA) signal line.
Overview
Background & Credits:
The relative strength index (RSI) is a momentum indicator used in technical analysis that was originally developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr. and introduced in his seminal 1978 book, “New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems.”.
Cutler created a variation of the RSI known as “Cutlers RSI” using a different formulation to avoid an inherent accuracy problem which arises when using Wilders method of smoothing.
Further developments in the use, and more nuanced interpretations of the RSI have been developed by Cardwell, and also by well-known chartered market technician, Constance Brown C.M.T., in her acclaimed book "Technical Analysis for the Trading Professional” 1999 where she described the idea of bull and bear market ranges for RSI, and while she did not actually reveal the formulas, she introduced the concept of “reverse engineering” the RSI to give price level outputs.
Renowned financial software developer, co-author of academic books on finance, and scientific fellow to the Department of Finance and Insurance at the Technological Educational Institute of Crete, Giorgos Siligardos PHD. brought a new perspective to Wilder’s RSI when he published his excellent and well-received articles "Reverse Engineering RSI [A Wilder Variation]" and "Reverse Engineering RSI II [The Revenge of the Indicators]" in the June 2003, and August 2003 issues of Stocks & Commodities magazine, where he described his methods of reverse engineering Wilders RSI.
Several excellent Implementations of the Reverse Wilders Relative Strength Index have been published here on Tradingview and elsewhere.
My utmost respect, and all due credits to authors of related prior works.
Introduction
It is worth noting that while the general RSI formula, and the logic dictating the UpMove and DownMove data series as described above has remained the same as the Wilders original formulation, it has been interpreted in a different way by using a different method of averaging the upward, and downward moves.
Cutler recognized the issue of data length dependency when using wilders smoothing method of calculating RSI which means that wilders standard RSI will have a potential initialization error which reduces with every new data point calculated meaning early results should be regarded as unreliable until enough calculation iterations have occurred for convergence.
Hence Cutler proposed using Simple Moving Averaging for gain and loss data which this Indicator is based on.
Having "Reverse engineered" prices for any oscillator makes the planning, and execution of strategies around that oscillator far simpler, more timely and effective.
Introducing the Reverse Cutlers RSI which consists of plotted lines on a scale of 0 to 100, and an optional infobox.
The RSI scale is divided into zones:
• Scale high (100)
• Bull critical zone (80 - 100)
• Bull control zone (62 - 80)
• Scale midline (50)
• Bear critical zone (20 - 38)
• Bear control zone (0 - 20)
• Scale low (0)
The RSI plots are:
• Cutlers RSI
• RSI MA signal line
• Test price RSI
• Alert level high
• Alert level low
The info box displays output closing price levels where Cutlers RSI value will crossover:
• Its previous value. (RSI [1])
• Bull critical zone.
• Bull control zone.
• Mid-Line.
• Bear control zone.
• Bear critical zone.
• RSI MA signal line
• Alert level High
• Alert level low
And also displays the resultant RSI for a user defined closing price:
• Test price RSI
The infobox outputs can be shown for the current bar close, or the next bar close.
The user can easily select which information they want in the infobox from the setttings
Importantly:
All info box price levels for the current bar are calculated immediately upon the current bar closing and a new bar opening, they will not change until the current bar closes.
All info box price levels for the next bar are projections which are continually recalculated as the current price changes, and therefore fluctuate as the current price changes.
Understanding the Relative Strength Index
At its simplest the RSI is a measure of how quickly traders are bidding the price of an asset up or down.
It does this by calculating the difference in magnitude of price gains and losses over a specific lookback period to evaluate market conditions.
The RSI is displayed as an oscillator (a line graph that can move between two extremes) and outputs a value limited between 0 and 100.
It is typically accompanied by a moving average signal line.
Traditional interpretations
Overbought and oversold:
An RSI value of 70 or above indicates that an asset is becoming overbought (overvalued condition), and may be may be ready for a trend reversal or corrective pullback in price.
An RSI value of 30 or below indicates that an asset is becoming oversold (undervalued condition), and may be may be primed for a trend reversal or corrective pullback in price.
Midline Crossovers:
When the RSI crosses above its midline (RSI > 50%) a bullish bias signal is generated. (only take long trades)
When the RSI crosses below its midline (RSI < 50%) a bearish bias signal is generated. (only take short trades)
Bullish and bearish moving average signal Line crossovers:
When the RSI line crosses above its signal line, a bullish buy signal is generated
When the RSI line crosses below its signal line, a bearish sell signal is generated.
Swing Failures and classic rejection patterns:
If the RSI makes a lower high, and then follows with a downside move below the previous low, a Top Swing Failure has occurred.
If the RSI makes a higher low, and then follows with an upside move above the previous high, a Bottom Swing Failure has occurred.
Examples of classic swing rejection patterns
Bullish swing rejection pattern:
The RSI moves into oversold zone (below 30%).
The RSI rejects back out of the oversold zone (above 30%)
The RSI forms another dip without crossing back into oversold zone.
The RSI then continues the bounce to break up above the previous high.
Bearish swing rejection pattern:
The RSI moves into overbought zone (above 70%).
The RSI rejects back out of the overbought zone (below 70%)
The RSI forms another peak without crossing back into overbought zone.
The RSI then continues to break down below the previous low.
Divergences:
A regular bullish RSI divergence is when the price makes lower lows in a downtrend and the RSI indicator makes higher lows.
A regular bearish RSI divergence is when the price makes higher highs in an uptrend and the RSI indicator makes lower highs.
A hidden bullish RSI divergence is when the price makes higher lows in an uptrend and the RSI indicator makes lower lows.
A hidden bearish RSI divergence is when the price makes lower highs in a downtrend and the RSI indicator makes higher highs.
Regular divergences can signal a reversal of the trending direction.
Hidden divergences can signal a continuation in the direction of the trend.
Chart Patterns:
RSI regularly forms classic chart patterns that may not show on the underlying price chart, such as ascending and descending triangles & wedges, double tops, bottoms and trend lines etc.
Support and Resistance:
It is very often easier to define support or resistance levels on the RSI itself rather than the price chart.
Modern interpretations in trending markets:
Modern interpretations of the RSI stress the context of the greater trend when using RSI signals such as crossovers, overbought/oversold conditions, divergences and patterns.
Constance Brown, CMT, was one of the first who promoted the idea that an oversold reading on the RSI in an uptrend is likely much higher than 30%, and that an overbought reading on the RSI during a downtrend is much lower than the 70% level.
In an uptrend or bull market, the RSI tends to remain in the 40 to 90 range, with the 40-50 zone acting as support.
During a downtrend or bear market, the RSI tends to stay between the 10 to 60 range, with the 50-60 zone acting as resistance.
For ease of executing more modern and nuanced interpretations of RSI it is very useful to break the RSI scale into bull and bear control and critical zones.
These ranges will vary depending on the RSI settings and the strength of the specific market’s underlying trend.
Limitations of the RSI
Like most technical indicators, its signals are most reliable when they conform to the long-term trend.
True trend reversal signals are rare, and can be difficult to separate from false signals.
False signals or “fake-outs”, e.g. a bullish crossover, followed by a sudden decline in price, are common.
Since the indicator displays momentum, it can stay overbought or oversold for a long time when an asset has significant sustained momentum in either direction.
Data Length Dependency when using wilders smoothing method of calculating RSI means that wilders standard RSI will have a potential initialization error which reduces with every new data point calculated meaning early results should be regarded as unreliable until calculation iterations have occurred for convergence.
开源脚本
秉承TradingView的精神,该脚本的作者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!您可以免费使用该脚本,但请记住,重新发布代码须遵守我们的网站规则。
You may contact me on Krown's Crypto Cave Discord: discord.gg/W9ettX54DF My Discord username is The Caretaker.
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并非旨在提供,也不构成TradingView提供或认可的任何形式的财务、投资、交易或其他类型的建议或推荐。请阅读使用条款了解更多信息。
开源脚本
秉承TradingView的精神,该脚本的作者将其开源,以便交易者可以查看和验证其功能。向作者致敬!您可以免费使用该脚本,但请记住,重新发布代码须遵守我们的网站规则。
You may contact me on Krown's Crypto Cave Discord: discord.gg/W9ettX54DF My Discord username is The Caretaker.
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
My Private indicators are available via :
krown-trading.teachable.com/?affcode=236462_mm1lb1_w
免责声明
这些信息和出版物并非旨在提供,也不构成TradingView提供或认可的任何形式的财务、投资、交易或其他类型的建议或推荐。请阅读使用条款了解更多信息。